Magnesium rods are frequently used in various industries and applications, but many people are unaware of the health hazards associated with them. In this comprehensive guide, we will cover everything you need to know about magnesium rods health hazards list, their applications, and how to safely handle them.
What Are Magnesium Rods?
Magnesium rods are solid, cylindrical rods made from magnesium metal. Magnesium is a lightweight, highly reactive metal that is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Due to its reactivity, magnesium rods must be handled with care to avoid health risks.
The Basics of Magnesium Rods
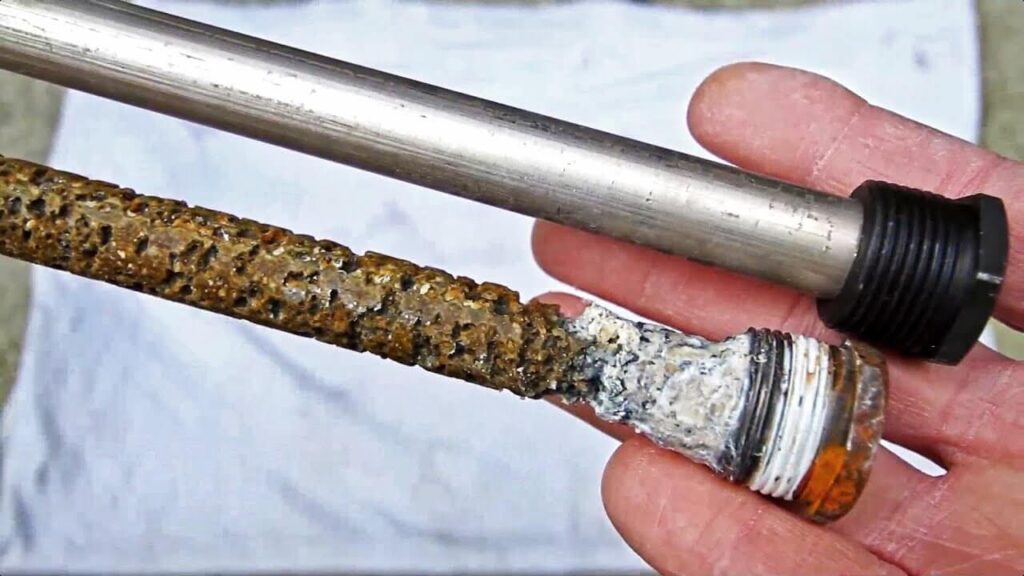

Magnesium rods are commonly used as sacrificial anodes in water heaters, boilers, and pipelines. Their ability to protect steel from corrosion makes them highly valuable. However, the chemical properties that make magnesium rods useful also contribute to their health hazards.
Common Applications of Magnesium Rods:
- Water heaters: Magnesium rods protect against corrosion.
- Aerospace and automotive industries: Due to their lightweight nature, magnesium rods are often used in aircraft and cars.
- Electronics: Magnesium rods serve as components in various electronic devices.
While these applications offer benefits, they come with certain health hazards that must be considered.
Health Hazards Associated with Magnesium Rods:
Magnesium rods health hazards list includes both short-term and long-term risks, ranging from mild skin irritation to serious respiratory issues. Let’s explore these hazards in detail.
Introduction to Magnesium Rods Health Hazards:
The hazards associated with magnesium rods stem from their reactivity. When magnesium comes into contact with water or air, it can ignite or react in ways that pose health risks. Prolonged exposure to magnesium dust or fumes can lead to respiratory problems, skin burns, and eye irritation.
Potential Health Hazards:
Below is the magnesium rods health hazards list:
- Respiratory problems: Inhaling magnesium dust or fumes can cause lung irritation and respiratory diseases over time.
- Skin burns: Direct contact with magnesium rods during chemical reactions may result in severe skin burns.
- Eye irritation: Magnesium dust can irritate the eyes, leading to discomfort and potential damage.
- Fire hazard: Magnesium can catch fire easily when exposed to air, posing a risk of burns or explosions.
1. Chemical Reactions:
Magnesium is highly reactive with other chemicals, especially in the presence of moisture. These reactions are part of the magnesium rods health hazards list and can result in fire or explosions if not managed properly.
2. Reactions with Water:
When magnesium rods come into contact with water, a vigorous chemical reaction occurs, producing hydrogen gas and magnesium hydroxide. This reaction is highly exothermic, meaning it releases heat and can potentially cause burns or even explosions.
How to Minimize Health Risks Associated with Magnesium Rods?
To minimize the risks, it is essential to follow proper handling and safety procedures. Below are some methods to ensure safe use of magnesium rods.
1. Proper Handling Procedures:
Magnesium rods health hazards list can be mitigated by ensuring that they are stored in a dry, cool environment. Proper storage reduces the risk of accidental chemical reactions.
2. Training and Awareness:
Workers handling magnesium rods should be properly trained to understand the risks and how to mitigate them. Knowledge of magnesium rods health hazards list can go a long way in preventing accidents.
3. Work Environment:
Ensure the work environment is safe for handling magnesium rods. Keep flammable materials away and always have fire extinguishers nearby. Additionally, magnesium rods health hazards list includes risks related to poor air quality, so proper ventilation is crucial.
4. Ventilation:
Ventilation is essential in any area where magnesium rods are handled. Poor ventilation can increase the risk of inhaling harmful magnesium dust and fumes, which are a significant part of the magnesium rods health hazards list.
5. Training and Procedures:
Employees should be well-versed in safety protocols for handling magnesium rods. Safety training should focus on the magnesium rods health hazards list, including fire hazards and how to respond to chemical reactions.
Environmental Considerations Regarding Magnesium Rods:
Magnesium rods can have environmental impacts as well. The magnesium rods health hazards list extends to the disposal of these rods, as improper disposal can lead to environmental pollution. Recycling or proper disposal methods should be followed to mitigate environmental risks.
Alternatives to Magnesium Rods:
For industries looking to avoid the magnesium rods health hazards list, several alternatives are available.
1. Aluminum Rods:
Aluminum rods are less reactive and can be used in many of the same applications as magnesium rods without the same health risks.
2. Stainless Steel Rods:
Stainless steel rods offer corrosion resistance and are safer to handle than magnesium rods.
3. Carbon Fiber Rods:
Carbon fiber is another alternative that is lightweight and durable, without the health hazards associated with magnesium.
4. Plastic Rods:
Plastic rods can also serve as alternatives in some applications, though they may not offer the same performance characteristics as magnesium rods.
Fire and Explosion Risks in Magnesium Rods Handling
Magnesium is highly flammable, especially when in powdered or shaved forms, and poses a severe fire and explosion risk. When magnesium rods are exposed to air, especially in environments where there’s moisture or extreme heat, the risk of ignition increases significantly.
Magnesium fires are unique in that they cannot be extinguished using traditional methods like water or standard fire extinguishers. In fact, adding water to a magnesium fire can exacerbate the situation, as it causes a chemical reaction that releases hydrogen gas, increasing the explosion risk.
Magnesium fires must be extinguished using special Class D fire extinguishers, which are designed for metal fires. The fire and explosion risks are one of the most critical entries in the magnesium rods health hazards list and should not be taken lightly in any industrial or laboratory setting.
Long-Term Health Effects of Magnesium Rod Exposure:
While acute exposure to magnesium rods can lead to immediate health hazards like burns and respiratory issues, long-term exposure may also result in more chronic health conditions.
Workers who are regularly exposed to magnesium dust or fumes may develop respiratory conditions such as bronchitis or pneumonitis over time. The fine particles of magnesium, if inhaled regularly, can settle in the lungs, leading to chronic inflammation.
Additionally, long-term skin exposure to magnesium can result in dermatitis, a condition where the skin becomes red, swollen, and irritated. Understanding the long-term implications of exposure is critical when discussing the full scope of the magnesium rods health hazards list, as it emphasizes the need for ongoing monitoring and safety precautions.
Legal and Regulatory Guidelines for Magnesium Rods:
Different countries and industries have specific legal frameworks and regulatory guidelines to minimize health risks associated with magnesium rods. For example, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for magnesium dust and fumes in workplaces.

These guidelines are critical to ensuring that workers are not overexposed to harmful levels of magnesium, and companies must follow strict protocols regarding ventilation, handling, and storage. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in legal penalties and increased health risks for workers.
Understanding the regulatory landscape is a key part of managing the risks identified in the magnesium rods health hazards list and helps industries implement effective safety measures.
Emergency Response and First Aid Procedures for Magnesium Rod Incidents:
In the event of an accident involving magnesium rods, quick and proper emergency response is essential. When magnesium comes into contact with skin or eyes, immediate flushing with large amounts of water is advised.
However, when magnesium ignites, specialized equipment is needed to extinguish the fire. Workers should be trained in first aid and emergency response specific to the hazards posed by magnesium rods. First aid kits in workplaces handling magnesium should include materials like burn ointments, sterile water, and proper dressings for chemical burns.
For inhalation of magnesium fumes, workers should be evacuated to an area with fresh air, and oxygen may need to be administered in severe cases. Establishing a clear emergency response plan is an essential addition to the magnesium rods health hazards list, as it can significantly reduce the severity of accidents when they occur.
FAQs:
1. What are magnesium rods used for?
Magnesium rods are primarily used in water heaters and as sacrificial anodes to prevent corrosion.
2. What health hazards are associated with magnesium rods?
The magnesium rods health hazards list includes respiratory issues, skin burns, and eye irritation, along with fire and explosion risks.
3. How can I safely handle magnesium rods?
Handle magnesium rods in a well-ventilated area, wear protective gear, and follow proper storage procedures.
4. What should be done if magnesium rods cause skin burns or respiratory issues?
Seek immediate medical attention and follow proper first aid procedures for chemical burns or respiratory distress.
5. Are there safer alternatives to magnesium rods?
Yes, alternatives such as aluminum, stainless steel, carbon fiber, and plastic rods can be used to avoid the magnesium rods health hazards list.
Conclusion:
Magnesium rods are useful in various industries, but they also pose significant health hazards. By understanding the magnesium rods health hazards list and following proper safety measures, the risks associated with magnesium rods can be minimized. Always ensure that you are well-informed about potential hazards and consider safer alternatives where possible.